The science is clear. Chronic inflammation and disease are intricately related. In fact, there is no doubt that chronic inflammation is a leading contributing factor to some of the most deadly health conditions. Chronic inflammation can have a detrimental effect on your overall health, making it important that you are aware of the steps that you can take to protect yourself.
Differentiating Between Chronic Inflammation and Acute Inflammation
 Have you ever noticed how your skin may turn red, swell and burn after an injury? This response is known as inflammation. Inflammation in itself is not always bad. This natural response is how the body reacts to a variety of illnesses or cellular injuries. Inflammation can be distinguished by redness, heat, pain, swelling, among other things. Some inflammation occurs internally, making it difficult to diagnose or notice.
Have you ever noticed how your skin may turn red, swell and burn after an injury? This response is known as inflammation. Inflammation in itself is not always bad. This natural response is how the body reacts to a variety of illnesses or cellular injuries. Inflammation can be distinguished by redness, heat, pain, swelling, among other things. Some inflammation occurs internally, making it difficult to diagnose or notice.
In order to understand inflammation completely, you need to know the difference between chronic inflammation and acute inflammation. Acute inflammation is what happens when the body triggers its defense system against an immediate threat to the body’s wellbeing, such as a virus, injury or bacteria. This type of inflammation is actually positive as it works to mitigate the harmful effects of foreign invaders so that the body can heal itself. Without this type of bodily response, injuries and infections could become deadly in a hurry.
Conversely, chronic inflammation is the result of harmful substances that accumulate in the body. This includes various toxins, environmental pollutants, excess fat cells, harmful free radicals and more. As these harmful substances accumulate, inflammation can lead to the development of fatty buildup in the arteries. Chronic inflammation contributes to a myriad of undesirable health conditions. Too much inflammation is a warning sign that there are deeper health issues that need to be addressed.
Chronic Inflammation and Disease
The relationship between chronic inflammation and disease is not in question. In fact, chronic inflammation is thought to be the root cause behind half of all fatalities each year across the globe. There is no shortage of diseases associated with chronic inflammation. Some of the most common diseases that are triggered as a result of chronic inflammation include cardiovascular diseases such as high blood pressure, lung issues such as asthma, mental illness, autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, some types of cancer, metabolic conditions such as Type 2 diabetes and various neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s. Aside from contributing to a host of health conditions, some experts even believe that chronic inflammation is the most significant contributor to the aging process.
Signs of Chronic Inflammation
While it is generally easy to spot the signs of acute inflammation, chronic inflammation can be more difficult to pinpoint. Depending on where the inflammation is flaring, the symptoms will vary in intensity and obviousness. Some of the most common signs of chronic inflammation include general fatigue, chest or abdominal pain, fever, rash, mouth sores and localized pain in the joints.
Your healthcare provider may order a blood test if they suspect that chronic inflammation may be the root cause of your health issues. This blood test, called a hsCRP, measures the C-reactive protein (CRP). This protein is a marker for inflammation, helping healthcare providers to ascertain if any of the organs in your body are experiencing inflammation.
How to Guard Against Chronic Inflammation
You are not powerless in the goal to control chronic inflammation. There are many actions that you can take now to guard against the development of this condition. Here are a few of the best ways that you can keep inflammation in check.
Eat Right
Your food choices go a long way in helping to stave off inflammation. Doctors recommend focusing the bulk of your diet on anti-inflammatory foods. Good choices include vegetables, fruit, beans, healthy fats and lean protein sources. You also need to be intentional about drinking plenty of water. Tea is another great all-natural beverage containing anti-inflammatory properties.
Exercise
As with most health conditions, a commitment to regular exercise can have a profound effect on how your body responds to inflammatory triggers. Regular exercise works to decrease inflammatory responses, helping to protect against a host of chronic health conditions.
Meditation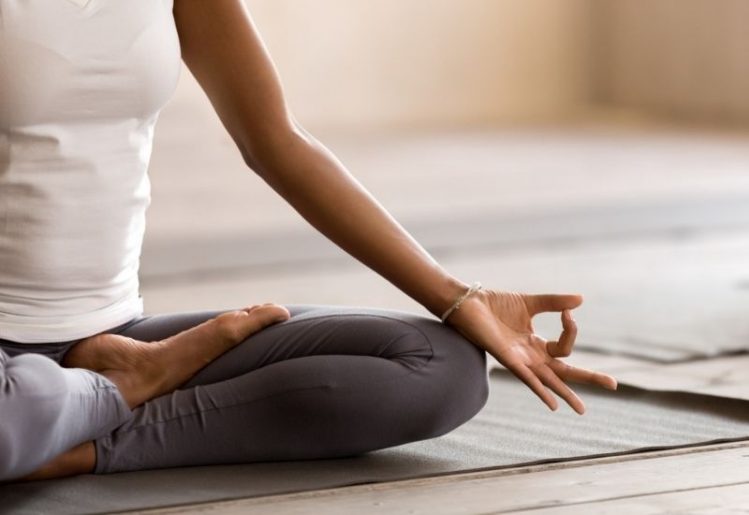
There is power in meditation when it comes to reducing the levels of inflammation in the body. Mind-body practices such as meditation are instrumental in suppressing the activity of the genes that are connected to inflammation. Regardless of whether you relax your body and mind through meditation or prayer, these practices have been shown to deactivate the triggers of inflammation.
There is no question that chronic inflammation is the root cause of a wide variety of health conditions. Understanding how to control this inflammation can boost your health and promote life longevity and vitality.


