Oxidative stress is a harmful process similar to “rusting” that results when there are more free radical molecules than antioxidant molecules in the body. Because free radicals have an odd electron count, they can initiate long-chain chemical reactions in the body. While these reactions can either be harmful or beneficial, they more often produce adverse effects, including a greater risk of disease. Research is taking a greater interest in cellular protection and the nutrients that help keep cells healthy as we learn more about the causes of disease.
Why is Cellular Protection Against Oxidative Damage Important?
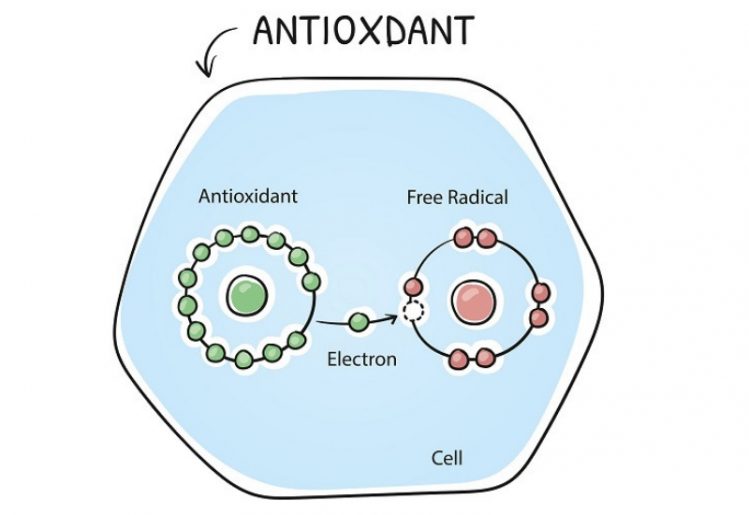 The threats to human health posed by an overabundance of free radicals are well known. Fortunately, compounds called antioxidants inhibit oxidation by lending an electron to a free radical without causing another odd electron count. This means an equal number of antioxidants can help negate the harmful effects that free radicals may have on the body.
The threats to human health posed by an overabundance of free radicals are well known. Fortunately, compounds called antioxidants inhibit oxidation by lending an electron to a free radical without causing another odd electron count. This means an equal number of antioxidants can help negate the harmful effects that free radicals may have on the body.
If there aren’t an equal or larger number of antioxidants than free radicals in the body, the free radicals are left to wreak havoc, causing cellular damage throughout the body. They do this by randomly attacking DNA and fatty tissue, although lipids and proteins are also at risk of damage.
As a result, the cells that are made up of these compounds are compromised and, as a greater number of cells are damaged, certain diseases are able to develop. A few medical conditions that can result from this type of cellular damage include:
- atherosclerosis
- cancer
- diabetes
- heart disease
- hypertension, or high blood pressure
- Parkinson’s disease
- Alzheimer’s disease
Which Nutrients Protect Against Cellular Damage?
While eating a plant-based diet can help you consume the nutrients your body needs to produce more antioxidants, you may still not have enough to combat the free radicals in your body.
Green Tea Catechins
When you steep green tea in hot water, the polyphenols, or catechins, in the leaves are extracted and infused into the water. Once consumed, these catechins provide a number of health benefits throughout the body. They have been found to be beneficial for helping to maintain healthy weight, maintaining healthy blood glucose levels, encouraging cellular health and protecting against heart disease and many other common conditions.
Catechins can benefit these areas of health because they have antioxidant properties that help counteract the activities of the free radicals. In this way, green tea catechins help protect cells from damage throughout the body.
Glutathione
While glutathione is another powerful and naturally occurring antioxidant that can help maintain good health, its levels in the body can be negatively impacted by poor diet, stress and environmental hazards. Research has also found that the level of glutathione in our bodies decreases as we age.
When we take a supplement that contains a sufficient quantity of this compound, it offers cellular protection by helping to counteract the oxidative stress that free radicals cause. As a result, conditions such as psoriasis, liver disease, insulin resistance, autoimmune disease, Parkinson’s disease and many other conditions may be positively impacted.
Pyrroloquinoline Quinone
The compound, commonly referred to as PQQ, is a naturally occurring compound that produces benefits similar to those of a vitamin, although it’s benefits are just now receiving recognition. It plays a part in promoting healthy cellular growth and development, helping to ensure that cells remain healthy and active for longer. It also possesses strong antioxidant properties and is more powerful than many known antioxidants, aiding in the fight to combat the effects that free radicals have on our cells.
Which Vegetables Provide the Best Protection?
Resverchron’s morning Green Cellular Protect capsule also contains a vegetable extract blend that provides the benefits of a range of vegetables in one capsule. The benefits of some of these vegetables are listed below.
Broccoli
 The most beneficial compounds in broccoli are carotenoids and sulforaphane, each of which are helpful in protecting cellular health. They do this by helping to flush harmful carcinogens out of the body. Additionally, broccoli extract is helpful in preventing the cell damage that can contribute to heart disease, cognitive decline and digestive problems.
The most beneficial compounds in broccoli are carotenoids and sulforaphane, each of which are helpful in protecting cellular health. They do this by helping to flush harmful carcinogens out of the body. Additionally, broccoli extract is helpful in preventing the cell damage that can contribute to heart disease, cognitive decline and digestive problems.
Brussels Sprouts
The antioxidants contained in Brussels sprouts help promote healthy cell growth, while also encouraging cardiovascular health and healthy cholesterol levels within normal ranges. Compounds found in Brussels sprouts are also helpful in flushing harmful toxins out of the body.
Carrots
The beta-carotene in carrots does more for us than just help with eyesight. Additionally, certain compounds in carrots can help improve oral health, promote liver health, boost overall immunity and protect the skin.
Leeks
Hailing from the same family as onions and garlic, leeks provide powerful antioxidants that help protect heart health, promote cellular health and help maintain healthy LDL cholesterol levels within normal ranges. They also improve gut health, promote a healthy pregnancy and encourage healthy weight maintenance by boosting metabolism.
Kale
This superfood contains a hefty supply of vitamin C, but that’s just the beginning of the benefits it provides. Kale contains compounds that possess anti-inflammatory and antioxidant qualities, helping to protect cellular health, support heart health and promote healthy vision. It also promotes healthy cell growth and aids in detoxification.
Garlic
This superfood is widely known for its antioxidant properties and is helpful in promoting cellular health. Additionally, it’s effective in protecting the skin against acne, psoriasis and other blemishes. It can also promote healthier hair growth.
More beneficial extracts found in the vegetable extract blend offered by Resverchron include barley, spinach, radish, beet, tomato, onion, cabbage, parsley, cauliflower, celery and yellow pepper. Each one of these extracts possess powerful healing properties that can help fight against the free radicals that contribute to cell damage.


